 |
Neuritic beta-amyloid plaques may be one of the first biomarker abnormalities in AD4,5
|
 |
Evidence of amyloid plaque accumulation has been shown to be
present when symptoms of cognitive impairment, due to AD,
appear;
may precede the appearance of clinical symptoms by approximately 20 years6-8 |
 |
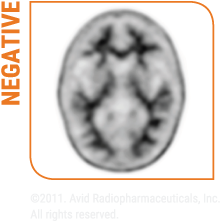
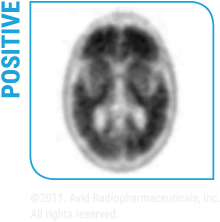
Amyvid scans are interpreted using a binary visual read
methodology (negative/positive)1
|

 |
 |
KNOW Unlikely
that the cause of their cognitive decline is due to AD1
|
 |
ACT
|
 |
 |
KNOW Evidence of moderate to
frequent beta-amyloid plaques in the brain is consistent with a
neuropathological diagnosis of AD1
|
 |
ACT
|
START TRAINING
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Risk for Image Misinterpretation and Other Errors
Radiation Risk
The most common adverse reactions reported in clinical trials were headache (1.8%), musculoskeletal pain (0.7%), blood pressure increased (0.7%), nausea (0.7%), fatigue (0.5%), and injection site reaction (0.5%) Please see Full Prescribing Information for Amyvid. AM HCP ISI 14SEP2022 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Amyvid is indicated for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging of the brain to estimate beta-amyloid neuritic plaque density in adult patients with cognitive impairment who are being evaluated for Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and other causes of cognitive decline. A negative Amyvid scan indicates sparse to no neuritic plaques and is inconsistent with a neuropathological diagnosis of AD at the time of image acquisition; a negative scan result reduces the likelihood that a patient's cognitive impairment is due to AD. A positive Amyvid scan indicates moderate to frequent amyloid neuritic plaques; neuropathological examination has shown this amount of amyloid neuritic plaque is present in patients with AD, but may also be present in patients with other types of neurologic conditions as well as older people with normal cognition. Amyvid is an adjunct to other diagnostic evaluations. Limitations of Use:
Amyvid for intravenous use is supplied in multidose vials containing |